Effective Fluridone Aquatic Herbicide – Control Weeds and Problem Plants Safely and Effectively With a Proven Leader
Fluridone is a Time Tested – Proven Weed Control Product Powerful Enough to Eliminate and Control Nuisance Aquatic Weeds Quickly and Effectively. A Trusted Ingredient used By Pond Managers Nationwide For Over 20 Years.
|
How Much fluridone Herbicide Do I Need?
An herbicide for management of aquatic vegetation in fresh water ponds, lakes, reservoirs, potable water sources, drainage canals and irrigation canals.Active Ingredient: Fluridone: 1-methyl-3-phenyl-5-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4(1H)-pyridinone………………… 41.7%Inert Ingredients………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 58.3%
Total………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 100.0%Contains 4 pounds active ingredient per gallon.Ponds: For fluridone labeling purposes, a pond is defined as a body of water 10 acres or less in size lakes or Reservoirs: For fluridone labeling purposes, a lake or reservoir is defined as greater than 10 acres in size. When only one-half or more of the lake or reservoir is treated, follow the Pond and Static Canal precautions.
Aquatic plant information
Depending on the use rate, water movement, application timing, weed growth stage and application method, fluridone will control, partially control, or will not control certain aquatic plant species. The table below categorizes the species when fluridone is applied under ideal application conditions at higher to maximum label rates. When lower rates are used, certain species in the controlled or partially controlled categories will show increased tolerance to fluridone. Aquatic plants not listed may also be controlled, partially controlled, or be tolerant to fluridone.
Before applying fluridone, identify the aquatic plants to determine their susceptibility to fluridone.
Vascular aquatic plants Controlled by fluridone
| floating plants | Emersed plants | Submersed plants | Shoreline Grasses |
|---|---|---|---|
| common duckweed (Lemna minor) | spatterdock (Nuphar luteum) | bladderwort (Utricularia spp.) | paragrass (Urochloa mutica) |
| water-lily (Nymphaea spp.) | common coontail (Ceratophyllum demersum) | ||
| common elodea (Elodea canadensis) | |||
| egeria, Brazilian elodea (Egeria densa) | |||
| fanwort, cabomba (Cabomba caroliniana) | |||
| hydrilla (Hydrilla verticillata) | |||
| naiad (Najas spp.) | |||
| pondweed (Potamogeton spp., except Illinois pondweed) | |||
| watermilfoil (Myriophyllum spp., except variable-leaf milfoil) |
Vascular aquatic plants partially controlled by fluridone
| floating plants | emersed plants | Submersed plants | Shoreline Grasses |
|---|---|---|---|
| common watermeal (Wolffia columbiana)† | alligatorweed (Alternanthera philoxeroides) | Illinois pondweed (Potamogeton illinoensis) | barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crusgalli) |
| American lotus (Nelumbo lutea) | limnophila (Limnophila sessiliflora) | giant cutgrass (Zizaniopsis miliacea) | |
| cattail (Typha spp.) | tapegrass, | reed canarygrass (Philaris arundinaceae) | |
| creeping waterprimrose (Ludwigia peploides) | American eelgrass (Vallisneria americana) | southern watergrass (Hydrochloa caroliniensis) | |
| parrotfeather (Myriophyllum aquaticum) | watermilfoil-variable-leaf milfoil (Myriophyllum heterophyllum) | torpedograss (Panicum repens) | |
| smartweed (Polygonum spp.) | |||
| spikerush (Eleocharis spp.) | |||
| waterpurslane (Ludwigia palustris) | |||
| watershield (Brasenia schreberi) |
† fluridone when used at the maximum use rate only provides partial control of this species.
| floating plants | emersed plants | Submersed plants | Shoreline Grasses |
|---|---|---|---|
| waterlettuce (Pistia stratiotes) | American frogbit (Limnobium spongia) | maidencane (Panicum hemitomon) | |
| arrowhead (Sagittaria spp.) | |||
| bacopa (Bacopa spp.) | |||
| big floatingheart, | |||
| banana lily (Nymphoides aquatica) | |||
| bulrush (Scirpus spp.) | |||
| floating waterhyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) | |||
| pickerelweed, lanceleaf (Pontederia spp.) | |||
| rush (Juncus spp.) | |||
| water pennywort (Hydrocotyle umbellata) |
*Note: fluridone does not control algae (Chara, Nitella, and single-cellular, colonial and filamentous species).
Preparation of fluridone Spray Solution
Determine the amount of area (acres) to be treated. Water depths in the treatment sites should also be known so that the correct application rate is selected.
Use the steps below to prepare spray mixtures of fluridone:
- Be sure to shake well the containers of fluridone before adding the product to the spray tank during mixing and loading operations.
- Add � to � the required amount of water to the spray tank. Begin agitation of the spray mixture and continue agitation during the mixing operations.
- Add the required amount of fluridone to the spray tank during the remainder of the mixing operation.
- Continue agitation of the spray mixture during the herbicide application operation.
Make surface or subsurface applications using conventional spray equipment. Use weighted trailing hoses to apply fluridone near the surface of the hydrosoil. Make applications with a spray volume of 5 to 100 gallons per acre. A metering system which mixes concentrated fluridone with water and then introduces this slurry into the suction side of the application equipment may also be used.
Note: fluridone is not corrosive to application equipment.
Tank Mix Recommendations
Tank mixes of fluridone with other aquatic herbicides and algaecides may provide greater efficacy and broader weed control or plant selectivity. Refer to the label for the herbicide or algaecide used as a tank mix with fluridone for use directions, precautions, and restrictions.
For additional application rate calculations, refer to the section How To Calculate Application Rates at the end of this label.Directions For Application Lakes and Reservoirs
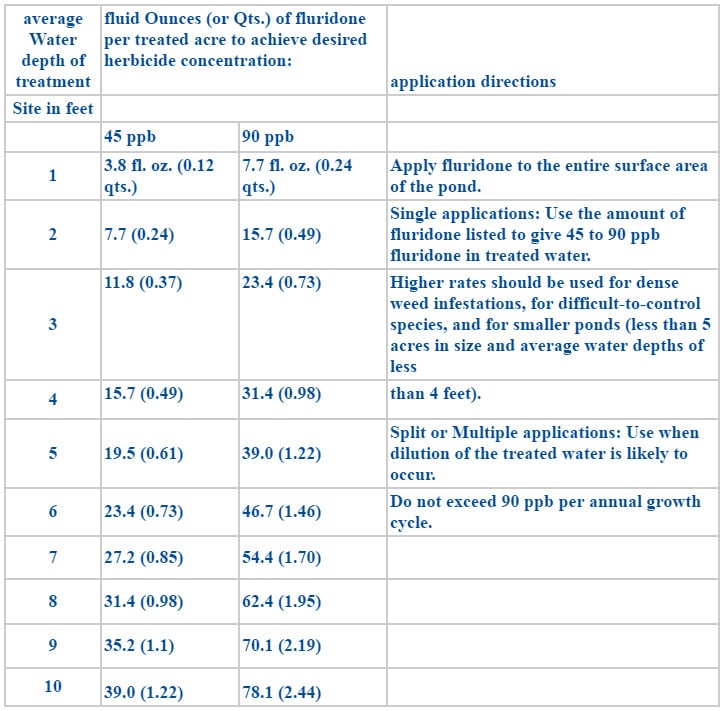
Fluridone dosage rate chart
fluridone is recommended for treatment of both whole lakes and reservoirs and partial areas of lakes or reservoirs (bays and coves). Target weeds in partial lake and reservoir treatments which are at least 5 acres in size are more effectively treated with fluridone than smaller size areas. Smaller treatment areas (less than 5 acres) or narrow strips such as boat trails or shorelines may not produce satisfactory results as fluridone may be diluted with untreated water. Due to a number of environmental factors, rate ranges are provided. Select the rates and application methods based on the specific goals of the aquatic plant management program at each different site.
Download Full Label Instructions **Here** Requires Acrobat Reader located **Here **

 Kills and Controls Duckweed, Milfoil, Watermeal and More
Kills and Controls Duckweed, Milfoil, Watermeal and More